Flutter/Android: Using AndroidX with a Flutter project
In today’s post, we’ll look at how to install AndroidX’s AppCompat library on a Flutter project.
Looking for how to install the Support Library (deprecated) instead?
Why?
If you’ve worked with Android projects in the past, you may be used to having the Support Library for various backwards-compatible goodies. Turns out the Support Library is now deprecated and projects are encouraged to use AndroidX instead.
Flutter developers chose not to include any of this in the base app project. It’s simply not needed for Flutter to work and increases the app size. So that makes a lot of sense.
But if you need to work on Android-specific code, chances are this library will be a requirement. So let’s see how to get it set up!
Prerequisites
This guide will assume:
- Your Flutter environment is set up (i.e. running
flutter doctordoesn’t report issues) - You have a working Flutter project you created earlier (I recommend using Android Studio to create the project. Check here for instructions)
- You have backed your project up. Copy it somewhere, commit to version control, anything. Do not proceed before you do that!
- Your app project is configured to build against
targetSdkVersion 28or above. If not, make that change now on yourbuild.gradlefile. This is required by AndroidX
Installing AndroidX AppCompat on your Flutter project
For this part, we’ll be using Android Studio (v3.4.1 as of writing this) as our tool of choice. While this can be done with Visual Studio Code, Android Studio makes it a lot easier on us.
Open the correct project
The main “trick” here is opening the correct project in Android Studio:
- On Android Studio, click
File > Open...and navigate to your Flutter project’s root. Don’t open it just yet! - In your project’s root folder, you will see a folder called
android. That’s the one we’re looking for - open it - You will notice this is just a regular Android project. If you never opened it before, you may see an error message:
Flutter SDK not found. Define location with flutter.sdk in the local.properties file.To fix it, as the message says, simply open yourlocal.propertiesfile in that same project and add:# This is the full path to your flutter SDK - the one you downloaded from flutter.io: # Example: flutter.sdk=/Users/caio/dev/flutter/ # flutter.sdk=<FLUTTER_SDK_PATH> - Android Studio should now be able to build it correctly
Install the AndroidX AppCompat library
Now that you have the right project opened and set up, installing the AppCompat library is simple.
Are you using the Support Library (com.android.support.*)? Migrate first:
If you already have the Support Library installed on your project, you will need to migrate the dependencies to AndroidX first. Luckily, Android Studio does that in one step:
- First of all, backup your whole project. If you use version control, commit or stash your changes. Push it if you use something like Github/Gitlab. If you don’t use version control (you should!), copy the entire project to a safe place.
- On Android Studio’s menu, go to
Refactor > Migrate to AndroidX. If you haven’t yet, take the offer and back everything up! Then press “Migrate”. Review the changes (if any) at the bottom and confirm if it look fine. If you get “No usages found”, you’re also good to go
If you were using appcompat from the Support Library, you’re done! Otherwise, read on:
If you are used to Gradle, you can skip the step-by-step option and go straight to option 2. It’s faster.
Option 1: Step-by-step, using Android Studio to help
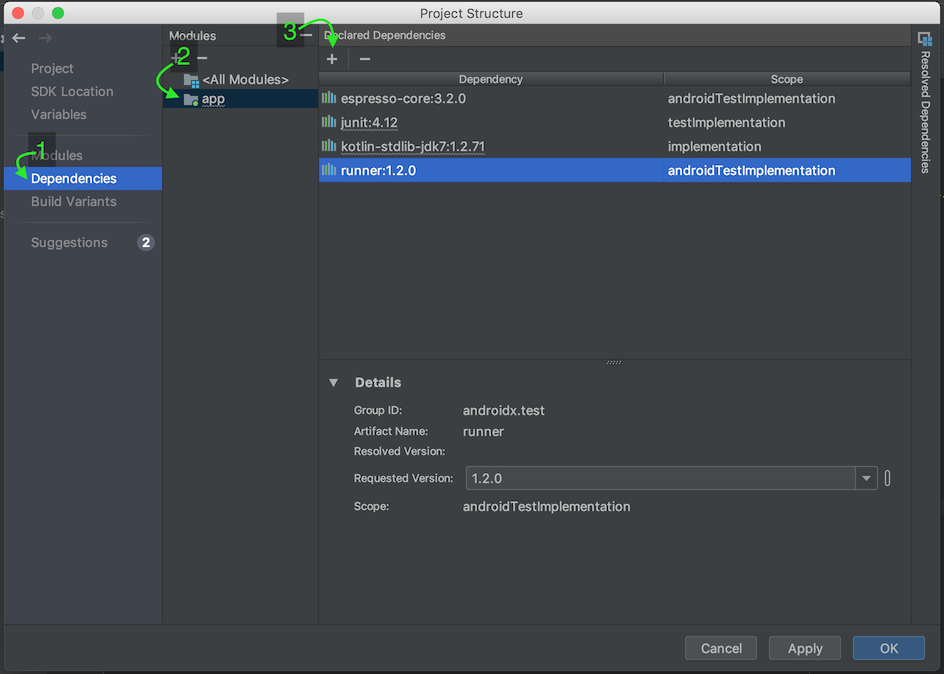
- On the Project navigation on the left, right click the main project module (it’s called
appby default) and selectOpen Module Settings - On the left hand side of the window that just opened, open the “Dependencies” tab and make sure your module is selected. The module is called
appby default - Click the
+at the top, underDeclared Dependenciesand selectLibrary Dependency - Type
androidx.appcompat:appcompatin the search and press the search button on the right. You should get only one result. Select it and choose the latest stable version on the right. It’s1.0.2at the time of writing this. - Press “Ok” and then “Ok” again to complete the change
In doubt? See this reference image:
Android Studio will trigger a Gradle sync for you.
Option 2: Quick way (add the dependency directly to build.gradle)
What all the steps above do is simply find the latest version of the library and add the dependency to the build.gradle file. If you are used to Gradle, you can achieve the same by editing the build.gradle file yourself. At the time of writing, the dependency looked like this:
implementation 'androidx.appcompat:appcompat:1.0.2' <-- Make sure to use the right version. This was up-to-date as of writing this article
That’s it!
If you used option 2, make sure to trigger a Gradle sync now. You should then have access to the same support tools as you expect from a regular Android project.
Caveats
If your project uses third-party libraries/plugins that depend on the old Support Library, these steps will likely break your project (this is why you back up!). You may need to update those libraries. If one or more of them don’t support AndroidX, it may not be possible to perform the migration just yet until they do.
Read more here: https://flutter.dev/docs/development/packages-and-plugins/androidx-compatibility
And as the official docs say: Happy Fluttering! :)
Bonus: Writing Android-specific code in your Flutter app project
If you open the android folder from the Android Studio window where the root Flutter project is open, it won’t work correctly. Android Studio won’t find the required SDKs and libs, and you won’t get any help from the IDE.
But now that you opened the correct project, you should be able to write code using all the right Android environment. Simply keep both windows open, and whenever you want to work on Android code, use the Android window. If you want to work on Flutter/dart code, use the Flutter window.
You can find more information on the Flutter Plugin for IntelliJ docs for Android.
Post by: Caio Landau Caio Landau
Caio Landau